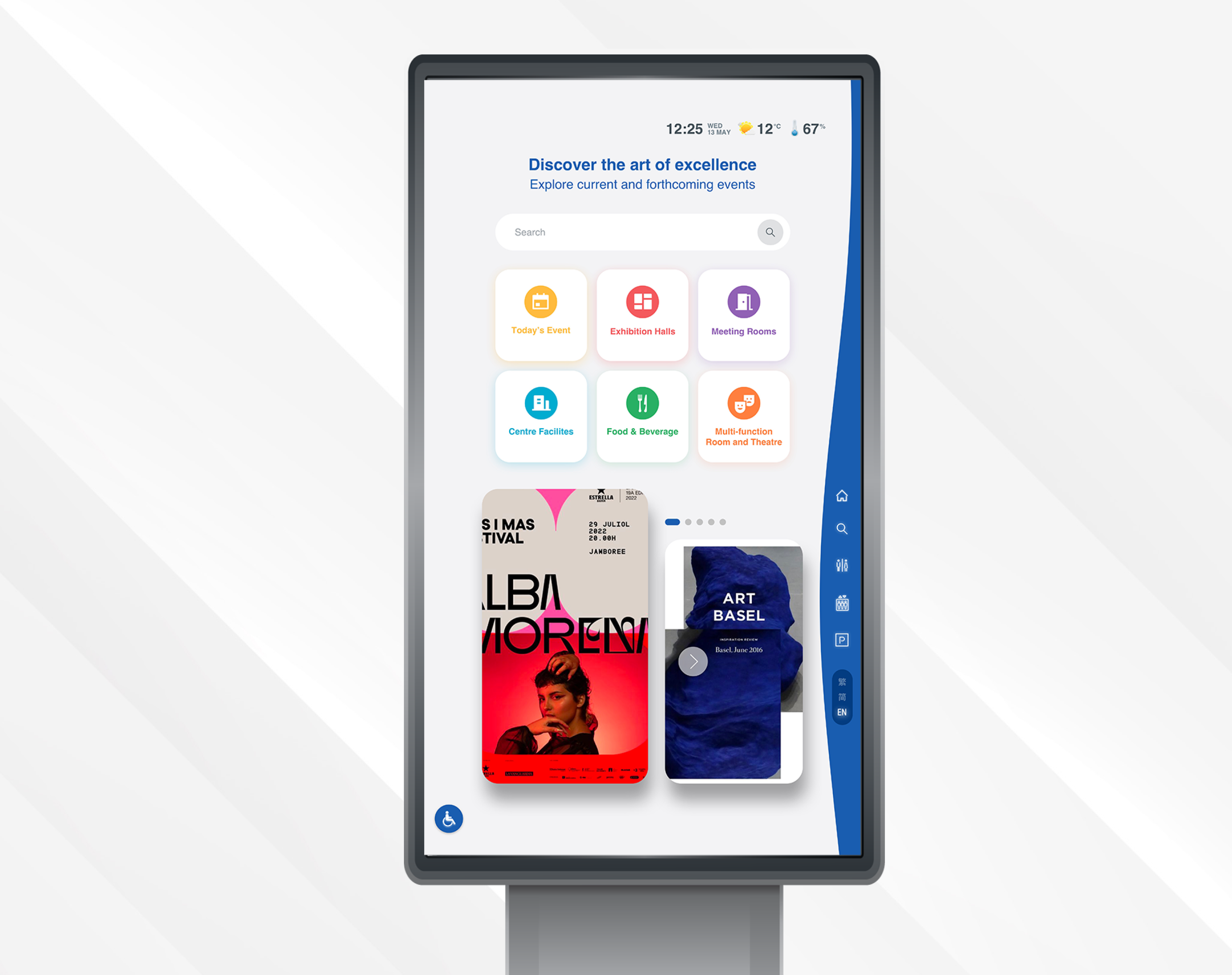
Wayfinding System Design
Designing an intuitive, information-driven wayfinding system that helps visitors effortlessly navigate the property using interactive maps and directories. Guiding users to their desired locations while optimizing their overall experience.
Tool
Figma
Client
Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Centre
My Role
UI/UX Designer
Duration
4-months
Human working memory retains navigation instructions is limited to roughly 15-30 seconds
— Cognitive Load Theory, John Sweller 1988
Pain points
Ephemeral Guidance and Cognitive Overload
Visitors lose critical navigation cues moments after leaving kiosks, forcing them to either retrace steps or seek assistance. Meanwhile, traditional static maps bombard users with excessive information, making route-finding mentally taxing rather than intuitive.
Accessibility Exclusion
Current systems lack multimodal support (voice, high-contrast, multilingual options), creating barriers for diverse user groups.
Target Audiences
Impromptu Explorers
-
Spontaneous visitors who prioritize discovery over efficiency
Often have flexible schedules (tourists, leisure seekers, creatives)
-
Serendipitous discovery tools that:
Highlight unique events
Suggest thematic routes (e.g., "Art Walk", "Hidden Gems")
Time-flexible planning:
"If you have 30/60/90 min" itinerary generators
Pause-and-resume navigation
Immersion-building features:
Augmented reality overlays with historical/artistic context
Gamified exploration (reward points for visiting zones)
Sniper Navigators
-
Goal-oriented professionals (business travelers, commuters)
Exhibit "tunnel vision" navigation patterns
Value speed and precision over exploration
-
Hyper-efficient routing:
1-click access to frequent destinations (restrooms, gates, exits)
Real-time congestion avoidance
Just-in-time information:
Dynamic ETAs accounting for walking speed
On-demand details (e.g., "Is this restroom wheelchair accessible?")
Error prevention:
Clear distinction between similar-sounding locations
"You are here" reliability indicators
Browsers
-
Decision-ambivalent visitors
Use "satisficing" behavior (first adequate option)
Vulnerable to choice paralysis
-
Comparative decision tools:
Side-by-side venue comparisons (ratings, wait times)
"Best match" algorithms based on stated preferences
Progressive filtering:
Dynamic category toggles
Social validation:
Crowd-sourced popularity heatmaps
Recent visitor check-ins/comments
Accessible Wayfinding Design Framework
This universally inclusive navigation system prioritizes accessibility through ergonomic, multimodal, and adaptive design to serve users of all abilities.
✅ Ergonomic Placement
Interactive elements positioned within 0.7m–1.2m for wheelchair users and children
✅ Multimodal Interaction
Auditory (voice guidance) input/output
Hands-free & motion-tolerant controls
Key Features
Simplified Navigation
Clear, icon-driven UI with minimal text to overcome language barriers
Color-coded zones and logical numbering for quick orientation
Intuitive Interaction
Touchscreen kiosks with responsive, large-tap targets
Real-time path visualization with step-by-step directions
Global Accessibility
Universal symbols and visual cues for cross-cultural usability
QR code for phone accessibility